Kubernetes - JSON Path
Alasta 20 Août 2024 kubernetes kubernetes json filter
Description : Kubernetes, JSON Path
Filtrage par le JSON Path
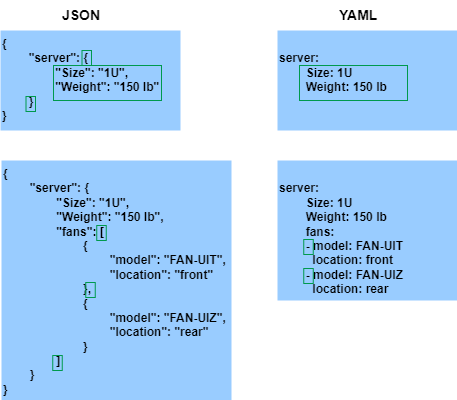
XML / JSON / YAML
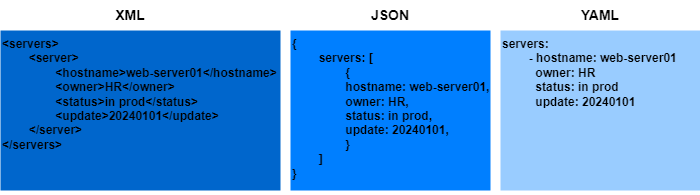
Différence entre le dictionnaire et le tableau
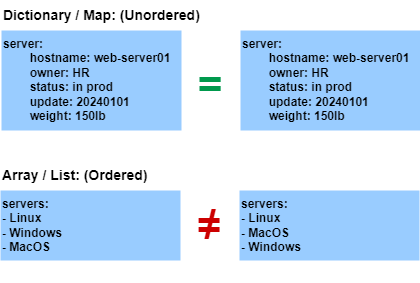
Dictionnaire / Map

Note: nombre d’espace important.
Clé valeur / Dictionnaire / Lists

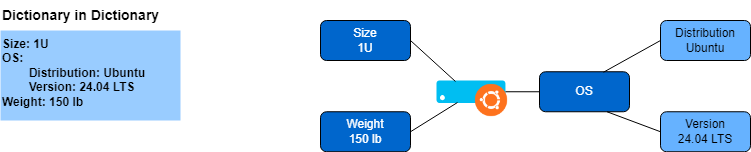
Dictionnaire dans un dictionnaire
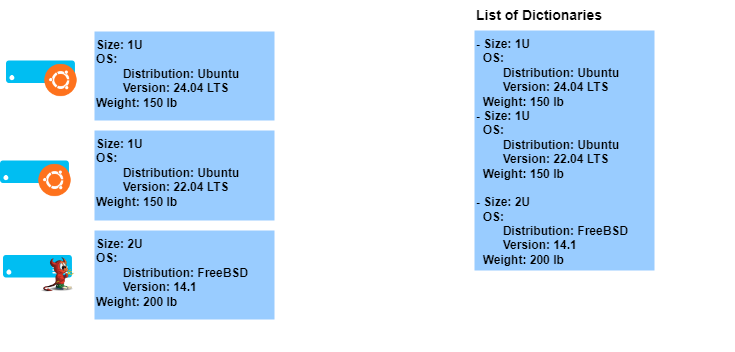
Liste de dictionnaire
YAML versus JSON
JSON Path
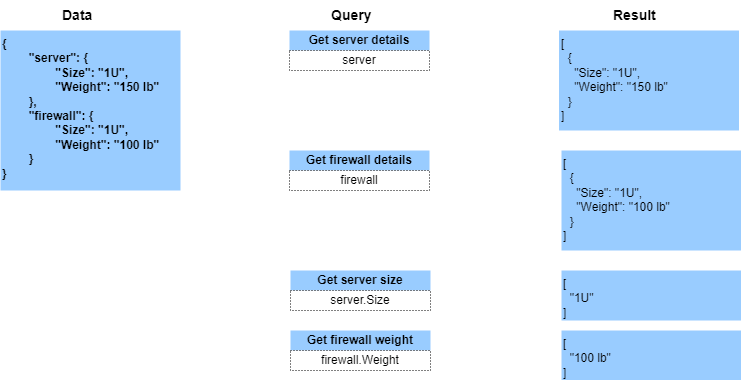
JSON Path - Dictionnaire

JSON Path - tableau
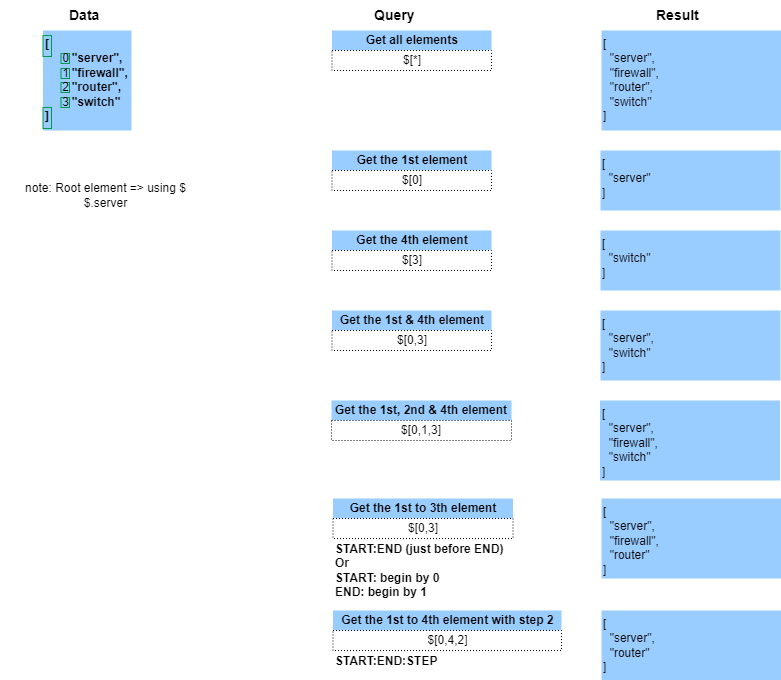
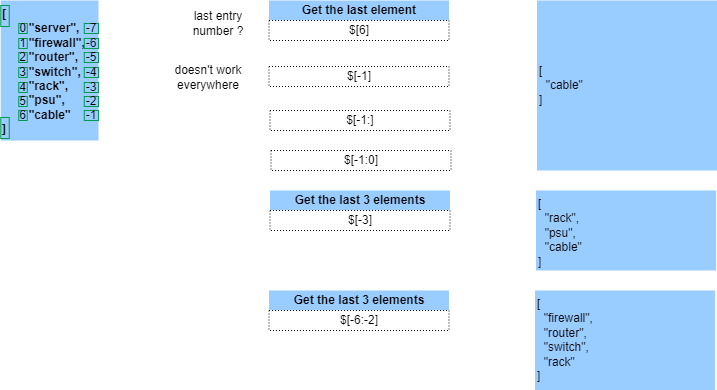
JSON Path - Dictionnaire & tableau

JSON Path - Critères


JSON Path - Wildcard avec un dictionnaire
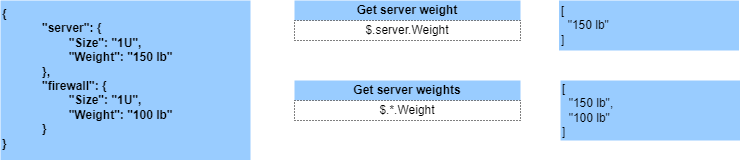
JSON Path - Wildcard avec un tableau

JSON Path avec kubernetes
Permet de filtrer les sorties de commandes sur de large data sets avec des centaines de nodes et de milliers de pods, déploiements, …
Informations sur les nodes
kubectl permet d’avoir des informations sur les nodes:
k get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
minikube Ready control-plane 151m v1.30.0
minikube-m02 Ready <none> 150m v1.30.0Il y a un peu plus d’options avec l’option -o wide
k get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
minikube Ready control-plane 152m v1.30.0 192.168.49.2 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS 5.15.0-69-generic docker://26.1.1
minikube-m02 Ready <none> 152m v1.30.0 192.168.49.3 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS 5.15.0-69-generic docker://26.1.1Il y a plus d’infos avec la sortie JSON mais moins lisible:
k get nodes -o json
{
"apiVersion": "v1",
"items": [
{
"apiVersion": "v1",
"kind": "Node",
"metadata": {
"annotations": {
"kubeadm.alpha.kubernetes.io/cri-socket": "unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock",
"node.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl": "0",
"volumes.kubernetes.io/controller-managed-attach-detach": "true"
},
"creationTimestamp": "2024-08-20T15:32:56Z",
"labels": {
"beta.kubernetes.io/arch": "amd64",
"beta.kubernetes.io/os": "linux",
"kubernetes.io/arch": "amd64",
"kubernetes.io/hostname": "minikube",
"kubernetes.io/os": "linux",
"minikube.k8s.io/commit": "5883c09216182566a63dff4c326a6fc9ed2982ff",
"minikube.k8s.io/name": "minikube",
"minikube.k8s.io/primary": "true",
"minikube.k8s.io/updated_at": "2024_08_20T17_32_59_0700",
"minikube.k8s.io/version": "v1.33.1",
"node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane": "",
"node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers": ""
},
"name": "minikube",
...Filtrage/limite sur les champs des sorties de commandes
Afficher que le nom des nodes
kubectl get nodes -o=jsonpath='{.items[*].metadata.name}'
minikube minikube-m02Afficher le nom des images
kubectl get nodes -o jsonpath='{.items[*].status.nodeInfo.osImage}'
Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTSTrier sur un champ
kubectl get pv --sort-by=.spec.capacity.storage
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS VOLUMEATTRIBUTESCLASS REASON AGE
pv-vol2 2Mi RWO Retain Available <unset> 79s
pv-vol1 10Mi RWO Retain Available <unset> 2m55s
pv-vol3 30Mi RWO Retain Available <unset> 73s
pv-vol4 40Mi RWO Retain Available <unset> 65sTrier sur un champ et sélectionner les colonnes de sortie
kubectl get pv --sort-by=.spec.capacity.storage -o=custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,CAPACITY:.spec.capacity.storage
NAME CAPACITY
pv-vol2 2Mi
pv-vol1 10Mi
pv-vol3 30Mi
pv-vol4 40Minote: permet de nommer les colonnes.
kubectl get nodes -o=jsonpath='{.items[*].metadata.name} {.items[*].status.capacity.cpu}'
minikube minikube-m02 4 4kubectl get nodes -o=jsonpath='{.items[*].metadata.name}{"\n"}{.items[*].status.capacity.cpu}'
minikube minikube-m02
4 4Le \t permet une tabulation.
Le \n fait un retour à la ligne.
Boucle permettant de changer le formattage
{range .items[*]}
{.metadata.name}{"\t"}{.status.capacity.cpu}{"\n"}
{end}kubectl get nodes -o=jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\t"}{.status.capacity.cpu}{"\n"}{end}'
minikube 4
minikube-m02 4